
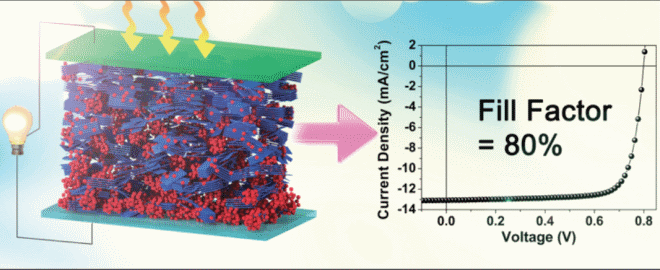
Current-voltage relationships measure the electrical characteristics of PV devices. Electrical power is the product of current and voltage. Researchers measure the performance of a photovoltaic (PV) device to predict the power the cell will produce. A high-efficiency cell will appear dark blue or black. Anti-reflection coatings and textured surfaces help decrease reflection. For example, untreated silicon reflects more than 30% of incident light. Reflection-A cell's efficiency can be increased by minimizing the amount of light reflected away from the cell's surface.Since much of the sunlight shining on cells becomes heat, proper thermal management improves both efficiency and lifetime. Extreme increases in temperature can also damage the cell and other module materials, leading to shorter operating lifetimes. Higher temperatures cause the semiconductor properties to shift, resulting in a slight increase in current, but a much larger decrease in voltage. Temperature-Solar cells generally work best at low temperatures.Indirect recombination is a process in which the electrons or holes encounter an impurity, a defect in the crystal structure, or interface that makes it easier for them to recombine and release their energy as heat. It is one of the fundamental factors that limits efficiency. Direct recombination, in which light-generated electrons and holes encounter each other, recombine, and emit a photon, reverses the process from which electricity is generated in a solar cell.

When an electron encounters a hole, they may recombine and therefore cancel out their contributions to the electrical current. Another such charge carrier is known as a "hole," which represents the absence of an electron within the material and acts like a positive charge carrier. Recombination-One way for electric current to flow in a semiconductor is for a "charge carrier," such as a negatively-charged electron, to flow across the material.The remainder have the right amount of energy to separate electrons from their atomic bonds to produce charge carriers and electric current. Some of the absorbed photons have their energy turned into heat. When light strikes the surface of a solar cell, some photons are reflected, while others pass right through. The sunlight that reaches the earth's surface has wavelengths from ultraviolet, through the visible range, to infrared. Wavelength-Light is composed of photons-or packets of energy-that have a wide range of wavelengths and energies.Designing with these factors in mind is how higher efficiencies can be achieved. Multiple factors in solar cell design play roles in limiting a cell's ability to convert the sunlight it receives. Not all of the sunlight that reaches a PV cell is converted into electricity. Improving this conversion efficiency is a key goal of research and helps make PV technologies cost-competitive with conventional sources of energy. The conversion efficiency of a photovoltaic (PV) cell, or solar cell, is the percentage of the solar energy shining on a PV device that is converted into usable electricity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
